Most of us wear an item of clothing made of cotton every day, sleep in cotton sheets or use cotton wool as part of our daily beauty routine.
But how much do we know about how cotton is grown and how it affects the environment?
Humans have used cotton for thousands of years.
Cotton balls have been found in Mexico that date back to 7000 years ago, and ancient civilisations such as the Egyptians first made cotton into cloth and clothing around 3000 BC.
Today, it’s estimated that around half of all textiles in the world are made from cotton.
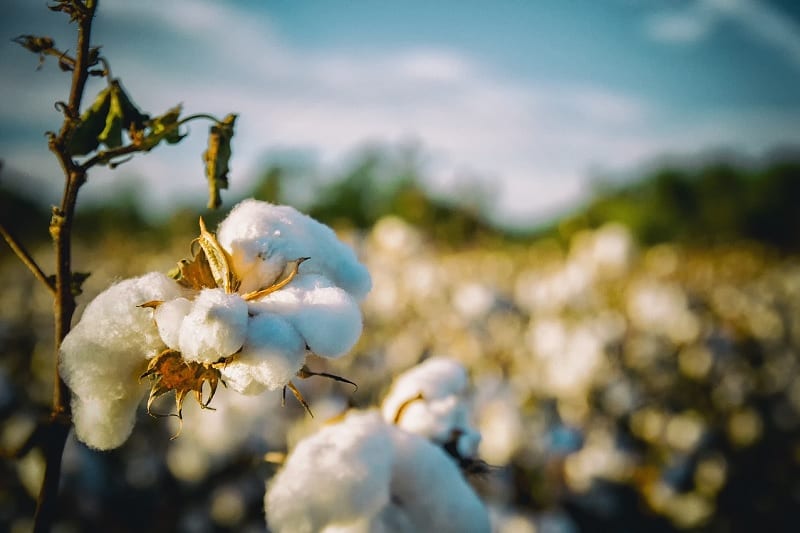
Cotton is the flower picked from cotton plants once it has turned white and fluffy.
It grows in several countries around the world including the USA, India and China and requires fertile, well drained soils and sunny, fairly dry conditions to grow well.
Once picked, the natural fibre from the plant is separated from the seed by a machine then used to make clothing and other products.
Cotton is strong and versatile, but also soft so it doesn’t irritate the skin, making it perfect for all kinds of clothing and household items.
Table of Contents
Is Cotton Biodegradable?
It’s estimated that around 80 billion items of clothing are bought every year around the world, but only 10% of our clothing is recycled with the rest ending up in landfill sites.
So, what happens to the clothing that ends up in landfill?
Cotton is a natural material made of cellulose, a polymer that makes the plant stiff and strong.
100% cotton is completely biodegradable, breaking down much quicker than clothes made of synthetic fibres such as polyester, which may remain in landfill sites for many years leaching out potentially harmful chemicals.
How Long Does Cotton Take to Biodegrade?
Cotton typically takes five to six months to break down, but is so biodegradable that it can potentially begin to decompose within a week.
The exact length of time can depend on the conditions where the cotton is left to biodegrade.
Cotton is biodegradable with oxygen (aerobically) and without oxygen (anaerobically).
The tightly packed conditions at landfills are anaerobic, keeping out water and oxygen, which means cotton will decompose much more slowly than on a compost heap.
Are Cotton Wool Balls Biodegradable?
Cotton wool balls and pads are used by many of us for our beauty routines, and the ones that are made from 100% cotton are fully biodegradable.
However, if they’ve come into contact with makeup or cleansers than aren’t 100% natural or organic, they can leave a build-up of chemicals in compost or landfill sites when they biodegrade.
It’s also worth noting that the names of these products can be misleading, and many modern cotton balls and pads are actually made out of cheaper, synthetic fibres such as polyester and nylon which won’t biodegrade as quickly, or contain chemicals, so always check the label to be sure.
Can 100% Cotton Be Composted?
Yes, 100% cotton can be composted fairly easily at home.
If you want to try composting 100% cotton yourself, here are a few tips:
- Cut or tear up the clothes before you add them to your compost bin to help them break down faster.
- Don’t compost anything that may have been stained by harmful chemicals or can’t be composted, such as oil, chemicals or paint (check the list of things you shouldn’t compost here).
- Remove any buttons, zips and other embellishments that aren’t made from 100% cotton.
- Adding wetter items such as fruit and vegetable peelings will help cotton to break down more quickly.
- Try not to add more than 25% of cotton items to your compost at any time.
Is Cotton Thread Biodegradable?
Sewing thread is essential for adding structure to our clothing, holding it together and for extra details.
100% cotton thread is natural and biodegradable, but even if an item of clothing is made from cotton (or even organic cotton), it doesn’t always mean that the thread used to sew it together hasn’t been made from non-biodegradable polyester, and it’s always worth checking the label when you buy something new.
If you’re composting old cotton clothes yourself, you may find that polyester threads will turn up still intact in your finished compost once the cotton clothing items have biodegraded.
Is Cotton Biodegradable in Water?
Cotton is biodegradable in all conditions, including water.
We may not be aware of it, but all of our clothing breaks down a little each time we wash it.
Each time we wash our clothes, microfibers are released washing down into drains and entering waterways.
Worryingly, synthetic microfibers will stay in the environment for a long time, and can reach our oceans where they can be consumed by sea life and enter our food chain.
Any cotton microfibers that enter our waterways will biodegrade fully and naturally.
Is Cotton Sustainable?
Cotton is a sustainable and renewable material making it “an excellent choice as an environmentally-friendly fibre throughout its entire product life cycle” (source).
A cotton plant has a short eight to nine month renewable life cycle, and other parts of the cotton plant are also “put to good use and are used in the production of foods, plastics and in paper products, according to the National Cotton Council of America” (source).
Cotton may sound like the perfect environmentally friendly material, but there are still concerns about the cotton industry.
Pesticides and insecticides have been used for years to grow cotton and control insect damage, and there are concerns about how harmful these chemicals are to the environment and human health.
Other concerns include soil erosion and the amount of water used in the growing process.
Many cotton-producing countries such as the USA and Australia are now finding ways of reducing the use of pesticides and water by using new technology, including the development of insect and drought-resistant varieties of cotton plants.
Clothing and household items made from organic cotton are becoming increasingly popular, and although this is a step in the right direction when it comes to using fewer pesticides, organic cotton currently needs more land, water and resources than non-organic cotton.
Summary
The biodegradability and renewability of cotton makes it a much better environmentally-friendly choice for clothing than clothes made from synthetic fibres.
However, we should all still try to reuse and recycle as much of our old cotton as we can before we throw it away or use it for compost.

Clare began her career as a technical writer, but since having her boys has worked mostly from home writing content for various websites, including health and beauty and educational resource sites.